.jpg?width=1400&height=425&name=Banner%20-%205%20Steps%20of%20Crack%20Injection%20-%20Drilling%20Holes%20(Continued).jpg)
.jpg?width=300&height=450&name=Body%20-%205%20Steps%20of%20Crack%20Injection%20-%20Drilling%20Holes%20(Continued).jpg) Let’s face it, most of the structures you drill through will be full of rebar. Rebar is the steel reinforcement that gives the structure its strength. Concrete protects the rebar by shielding it from moisture, and the high pH of concrete keeps the rebar from rusting. However, once a crack forms it allows more water and environmental gasses to reach the area surrounding the rebar. Carbonation of the concrete can now occur which causes the pH to drop and the corrosion process to begin. The rust expands and takes up 15 times the volume of the un-corroded steel which causes tensile forces to work against the concrete eventually resulting in additional cracking and spalling. Hopefully, you will be called in to fix the leaks before much of this damage occurs.
Let’s face it, most of the structures you drill through will be full of rebar. Rebar is the steel reinforcement that gives the structure its strength. Concrete protects the rebar by shielding it from moisture, and the high pH of concrete keeps the rebar from rusting. However, once a crack forms it allows more water and environmental gasses to reach the area surrounding the rebar. Carbonation of the concrete can now occur which causes the pH to drop and the corrosion process to begin. The rust expands and takes up 15 times the volume of the un-corroded steel which causes tensile forces to work against the concrete eventually resulting in additional cracking and spalling. Hopefully, you will be called in to fix the leaks before much of this damage occurs.
Once you are on the job site, this slow process of decay does not really affect you (unless the concrete is spalling off as you drill). Your issue with the rebar is that it will stop your drill bit from penetrating the crack. The cracks will often follow the rebar, especially if there is not adequate coverage of concrete over the rebar. Shallow rebar is a huge contributing factor to cracks in concrete.
At this point, all you care about are two things. First, how do you know if you have hit rebar? Second, if you have hit it, what do you do next?
After drilling many thousands of holes, as I have over my career, I pretty much know when I have hit rebar. Here are a few things to look for:
- The forward progress of drilling has stopped.
- The sound of the drilling changes.
- The quantity of drilling dust is reduced.
- If you are not sure, put your hand out to catch some of the drilling dust coming out of the drill hole. Observe it for metal shavings.
Given enough time and effort, you can drill through rebar. However, I wouldn’t recommend this as a general practice. It takes a lot of time, weakens the structure you are trying to protect, and...have you bought a drill bit lately? Steel is expensive! Try this instead:
- Move further away from the crack and try again (adjust your drilling angle).
- Move closer to the crack and try again (adjust your drilling angle).
- Move parallel to the crack and try again.
- Move to the other side of the crack and try again.
As a last resort, drill straight into the crack. This is not the ideal situation, but if you can drill deep enough to get an injection port installed, then you might be able to successfully seal the leak.
Now that the surface of your concrete looks like Swiss cheese, it is time to go get that bag of fast-set hydraulic cement you brought along for just this purpose. Try to patch it up before you begin injection because some of those abandoned holes are libel to have hit pay dirt. If you don’t seal them up then you will have foam or resin leaking out of the holes.
Hitting rebar is not fun and can be frustrating. The key is to expect it and try to think three-dimensionally. See if you can visualize what is going on behind the concrete. This is one of the keys to becoming a really good injection technician.
5 Steps of Crack Injection - Overview
5 Steps of Crack Injection - 1. Drilling Holes
5 Steps of Crack Injection – 1. Drilling Holes (Continued)
5 Steps of Crack Injection – 2. Flushing Holes
5 Steps of Crack Injection – 3. Installing Ports
5 Steps of Crack Injection – 4. Flushing Cracks
5 Steps of Crack Injection – 5. Injecting Resin



 Inflow and Infiltration (I&I)
Inflow and Infiltration (I&I)

 I remember my first day on the job back in June of 1985. We were working nights in the subway tunnels of Atlanta, sealing leaks in the ceiling. The crew handed me a 30-pound hammer drill and told me to drill holes in the ceiling at a 45-degree angle. Sure, what the heck is a 45-degree angle? I put on a lot of muscle that summer drilling overhead and hauling 50-pound pails of resin all over the Southeastern U.S.
I remember my first day on the job back in June of 1985. We were working nights in the subway tunnels of Atlanta, sealing leaks in the ceiling. The crew handed me a 30-pound hammer drill and told me to drill holes in the ceiling at a 45-degree angle. Sure, what the heck is a 45-degree angle? I put on a lot of muscle that summer drilling overhead and hauling 50-pound pails of resin all over the Southeastern U.S.
 The approach and departure slabs adjacent to a bridge in McKenzie County, North Dakota had settled, leading to an uneven and hazardous road surface. A geotechnical contractor was brought in to level the road surface and mitigate any further settlement.
The approach and departure slabs adjacent to a bridge in McKenzie County, North Dakota had settled, leading to an uneven and hazardous road surface. A geotechnical contractor was brought in to level the road surface and mitigate any further settlement. 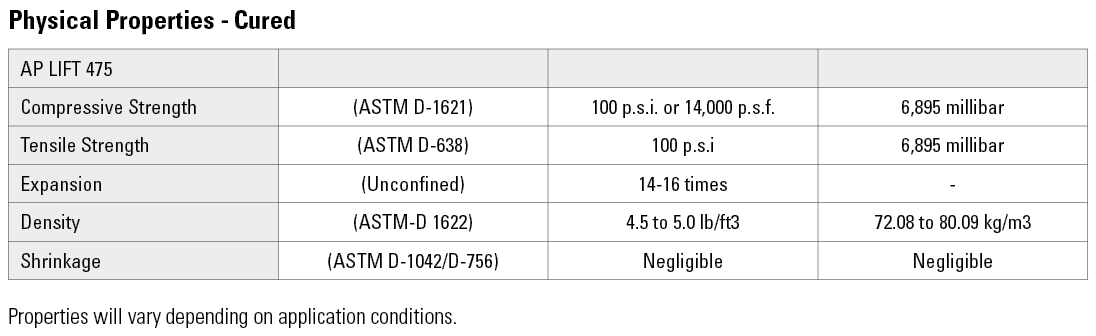


 A general contractor working on new luxury apartment construction in Queens, NY reached out to a local leak seal specialist after discovering hairline cracks in the base joint of a fire protection storage tank. (A fire protection storage tank stores water for use in fire suppression systems.)
A general contractor working on new luxury apartment construction in Queens, NY reached out to a local leak seal specialist after discovering hairline cracks in the base joint of a fire protection storage tank. (A fire protection storage tank stores water for use in fire suppression systems.)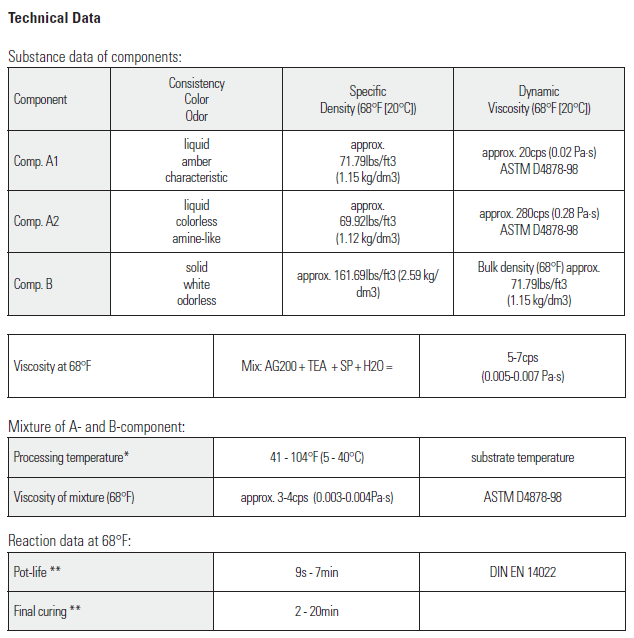


 There are five basic steps to be done when placing a crack injection. This is crack injection 101. Learn these steps and you will be well on your way to understanding what it takes to seal a water leak in concrete with products such as
There are five basic steps to be done when placing a crack injection. This is crack injection 101. Learn these steps and you will be well on your way to understanding what it takes to seal a water leak in concrete with products such as 
 Hydrophobic polyurethanes naturally repel water (similar to the way oil would repel water and stay separate if you were trying to mix them in a glass). These products push water out of the area in question as they expand. Hydrophobics are used with catalysts which allow you to adjust the set time. They also have zero shrinkage after curing.
Hydrophobic polyurethanes naturally repel water (similar to the way oil would repel water and stay separate if you were trying to mix them in a glass). These products push water out of the area in question as they expand. Hydrophobics are used with catalysts which allow you to adjust the set time. They also have zero shrinkage after curing.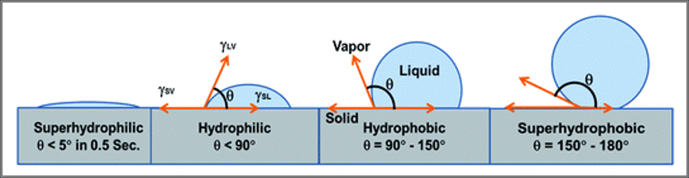

 Carrington Woods Lake Dam is located in Baldwin County, Georgia. A consulting firm collaborating with a general contractor called in geotech specialists
Carrington Woods Lake Dam is located in Baldwin County, Georgia. A consulting firm collaborating with a general contractor called in geotech specialists 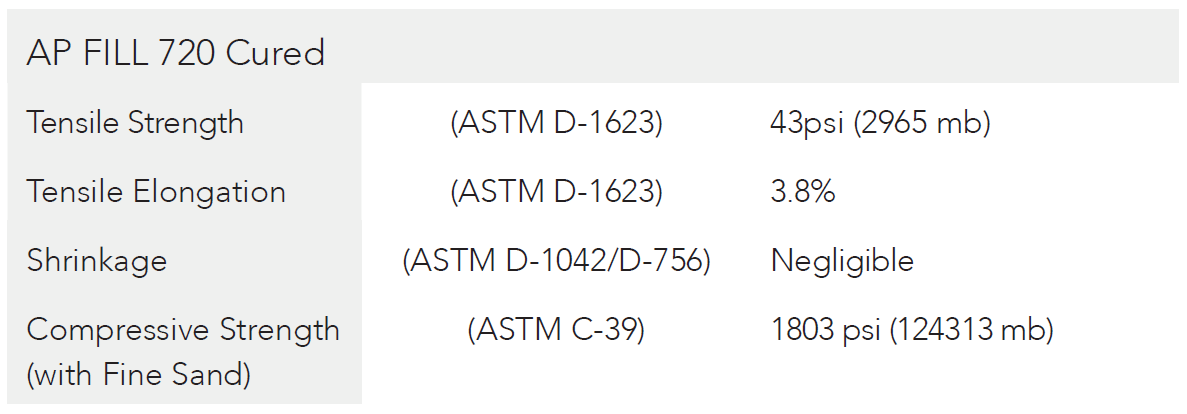

 When the residue of plants or animals is converted into soil, the process is known as decomposition. Bacteria, fungi, and worms break down this residue, taking nutrients from them and leaving the remaining portion. Organic molecules are broken down into simpler inorganic molecules. This biological process changes the makeup of the soil and can therefore lead to soil instability.
When the residue of plants or animals is converted into soil, the process is known as decomposition. Bacteria, fungi, and worms break down this residue, taking nutrients from them and leaving the remaining portion. Organic molecules are broken down into simpler inorganic molecules. This biological process changes the makeup of the soil and can therefore lead to soil instability.

 What is freezing and thawing?
What is freezing and thawing?