The terms hydrophobic and hydrophilic may not mean anything to the average person. But, to a contractor, these terms can mean a world of difference. Hydro means water while phobic means “to fear” and philic means “to love”. Alchatek offers both hydrophobic and hydrophilic polyurethanes, so it is important to be aware of the differences between the two types.
Hydrophobic Polyurethanes
 Hydrophobic polyurethanes naturally repel water (similar to the way oil would repel water and stay separate if you were trying to mix them in a glass). These products push water out of the area in question as they expand. Hydrophobics are used with catalysts which allow you to adjust the set time. They also have zero shrinkage after curing.
Hydrophobic polyurethanes naturally repel water (similar to the way oil would repel water and stay separate if you were trying to mix them in a glass). These products push water out of the area in question as they expand. Hydrophobics are used with catalysts which allow you to adjust the set time. They also have zero shrinkage after curing.
Check out these hydrophobic polyurethanes:
- Spetec PUR HighFoamer
- Spetec PUR F400
- Spetec PUR H100
- Spetec PUR H200
- AP Fill 420
- AP Deep Lift® 420
- AP Lift 430
- AP Lift 435
- AP Lift 440
- AP Lift 475
- AP Soil 600
- AP Fill 700
- AP Fill 720
Hydrophilic Polyurethanes
Hydrophilic polyurethanes naturally mix with water before curing (similar to the way gin and tonic mix thoroughly in a glass). This characteristic allows for a very strong chemical and mechanical bond, as water helps pull the material into the pores of the concrete. These products do not require a catalyst. You can pump them straight out of the pail.
Check out these hydrophilic polyurethanes:
Don't Oversimplify These Concepts
Don't get caught in the trap of oversimplifying hydrophilic vs. hydrophobic. There are varying degrees of each (see chart below for more information on how this is measured).
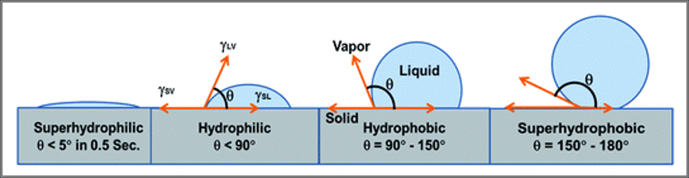
Some hydrophilic materials will keep absorbing water (10-15 times their original volume). Others (such as Spetec PUR GT500) only absorb as much water as is necessary for their reaction and then they reject the rest. Yes, hydrophilic gels will shrink like crazy in the absence of water, but Spetec PUR GT500 won't. It is completely safe to use in a dry environment.




 Carrington Woods Lake Dam is located in Baldwin County, Georgia. A consulting firm collaborating with a general contractor called in geotech specialists
Carrington Woods Lake Dam is located in Baldwin County, Georgia. A consulting firm collaborating with a general contractor called in geotech specialists 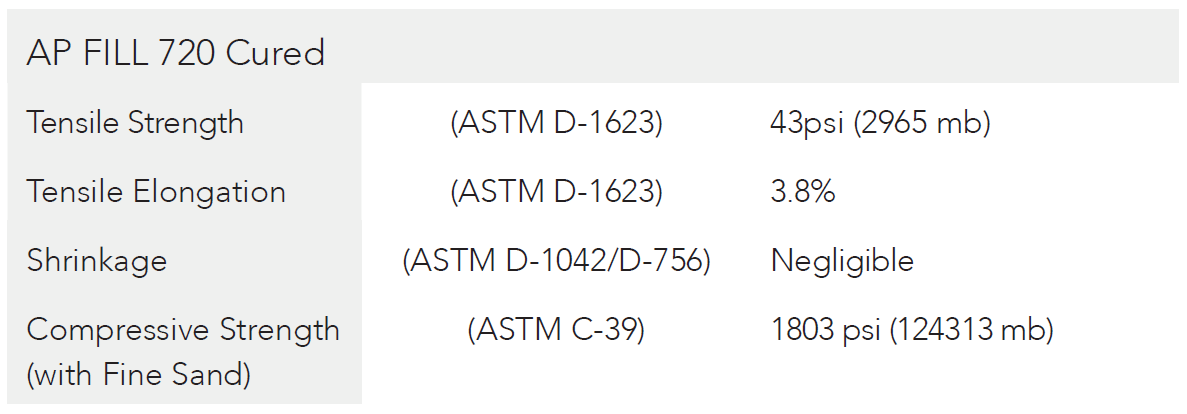

 When the residue of plants or animals is converted into soil, the process is known as decomposition. Bacteria, fungi, and worms break down this residue, taking nutrients from them and leaving the remaining portion. Organic molecules are broken down into simpler inorganic molecules. This biological process changes the makeup of the soil and can therefore lead to soil instability.
When the residue of plants or animals is converted into soil, the process is known as decomposition. Bacteria, fungi, and worms break down this residue, taking nutrients from them and leaving the remaining portion. Organic molecules are broken down into simpler inorganic molecules. This biological process changes the makeup of the soil and can therefore lead to soil instability.

 What is freezing and thawing?
What is freezing and thawing?
 Many types of infrastructure, including roads, bridges, and buildings, depend on compacted soil in order to stay in place. Therefore, in order for these structures to last, a specific degree of compaction must be achieved. When soil does not adequately compact, the problem is known as poor compaction, and that can lead to more serious issues. Concrete repair contractors always need to be on the lookout for signs of poor compaction which include settling slabs, cracking foundations, and dips in roadways and railroads.
Many types of infrastructure, including roads, bridges, and buildings, depend on compacted soil in order to stay in place. Therefore, in order for these structures to last, a specific degree of compaction must be achieved. When soil does not adequately compact, the problem is known as poor compaction, and that can lead to more serious issues. Concrete repair contractors always need to be on the lookout for signs of poor compaction which include settling slabs, cracking foundations, and dips in roadways and railroads.
 What is erosion?
What is erosion?
 Unstable soil can be defined as soil that will not stay in place on its own and therefore requires extra support. It should be noted that unstable soil can threaten the stability, security, and safety of infrastructure and can damage, degrade, and even destroy a number of structures, such as buildings, bridges, and roads.
Unstable soil can be defined as soil that will not stay in place on its own and therefore requires extra support. It should be noted that unstable soil can threaten the stability, security, and safety of infrastructure and can damage, degrade, and even destroy a number of structures, such as buildings, bridges, and roads.
 Raising Concrete with Confidence
Raising Concrete with Confidence

 If you're a leak seal contractor, you may be familiar with this situation: A property owner with leaking concrete calls you up and says, "Hey, everything is dry right now, so I want to get someone out here to go ahead and waterproof the structure." Attempting a waterproofing job when the structure is completely dry is not recommended.
If you're a leak seal contractor, you may be familiar with this situation: A property owner with leaking concrete calls you up and says, "Hey, everything is dry right now, so I want to get someone out here to go ahead and waterproof the structure." Attempting a waterproofing job when the structure is completely dry is not recommended.